As technology advances, the demand for smart home and industrial automation devices is rising. One of the standout innovations in this space is the TIDC-SMARTPLUG-WIFI, a smart plug that integrates remote disconnect capabilities with Wi-Fi connectivity. This device offers a comprehensive energy measurement and management solution, catering to modern smart homes, appliances, and building automation systems.
This blog explores the key features, design, and functionality of the TIDC-SMARTPLUG-WIFI, demonstrating its potential to revolutionize energy management.
Key Features
The TIDC-SMARTPLUG-WIFI is designed to provide robust energy management solutions with several key features:
1. Wi-Fi Connectivity: The smart plug uses SimpleLink™ Wi-Fi, which operates over IEEE-802.11 b/g/n networks. This allows for seamless connectivity from any smartphone, tablet, or computer through a standard web browser. This feature facilitates easy monitoring and control of energy consumption remotely.
2. Energy Measurement: The smart plug is equipped with single-phase energy measurement capabilities. It calculates key metrics such as RMS current, RMS voltage, active and reactive power, energy consumption, power factor, and frequency. This comprehensive energy monitoring allows users to track their energy usage in real-time.
3. Remote Connect/Disconnect: A solid-state relay integrated within the plug provides remote connect and disconnect capabilities. This feature is particularly useful for managing devices from a distance, ensuring convenience and enhancing energy-saving efforts.
4. Compact Design: The smart plug boasts a compact physical design with minimal Bill of Materials (BOM) components. This not only reduces manufacturing costs but also minimizes system power consumption, thanks to the use of low-power components and an efficient power supply.
5. Firmware and Application Support: The system design includes tested firmware for energy measurement, Wi-Fi connectivity, and relay control. Additionally, an Android-based demo application and user guide are provided, making it easier for users to understand and utilize the plug’s capabilities.
Design Overview
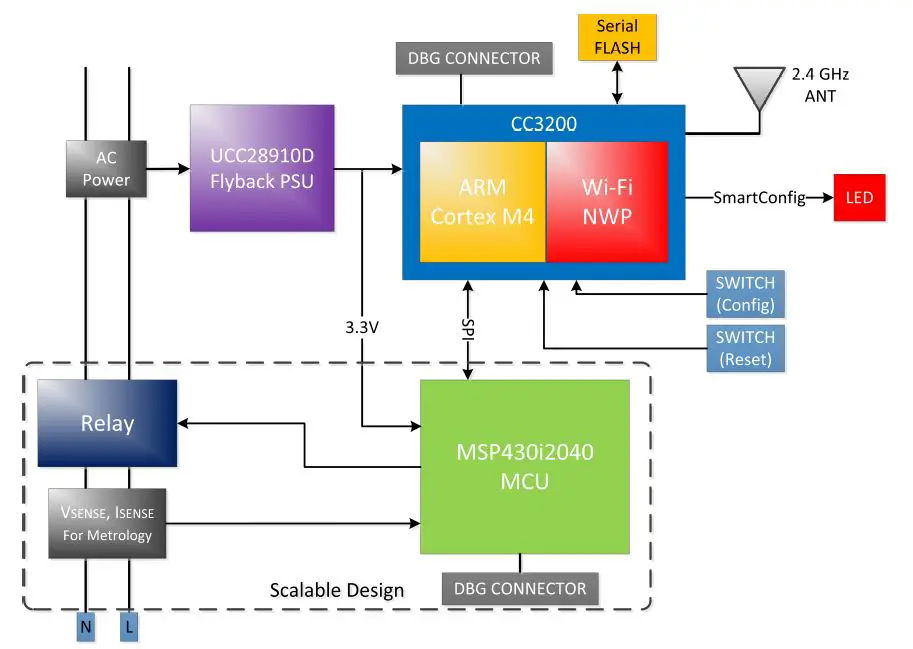
The TIDC-SMARTPLUG-WIFI smart plug leverages Texas Instruments’ (TI) competitive portfolio to deliver a unique product that offers both innovative features and cost savings. At its core, the smart plug utilizes the MSP430i2040 microcontroller to monitor energy consumption and control the high-voltage side of the design. This data is transmitted via a CC3200 microcontroller, which handles Wi-Fi communication to both local devices and cloud servers.
The power supply for the smart plug is designed with a compact and efficient primary side regulated flyback power supply unit (PSU) using the UCC28910D. This PSU ensures that the system remains energy-efficient while providing the necessary power for all components. A solid-state relay within the design allows the plug to control the connected load based on its energy consumption.
Block Diagram of TIDC-SMARTPLUG-WIFI
Connection and Safety Features
The smart plug is designed to connect easily to a North American NEMA 15 power outlet, facilitating straightforward integration with various devices. This design includes both male and female connectors to ensure compatibility and ease of use. Safety is a priority, with the smart plug featuring a simple enclosure to insulate users from potential high-voltage exposure. The electronics are pre-designed to accommodate international voltages, ensuring versatility in global markets with only minimal mechanical adjustments required.
Embedded Metrology and Analog Input Design
To accurately measure energy usage, the smart plug employs a sophisticated analog front-end for both voltage and current inputs. The MSP430i204x microcontroller features a differential Sigma-Delta Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC), which requires the input voltages to be scaled down to within ±928 mV.
For voltage inputs, the design includes spike protection varistors, a voltage divider network, and an RC low-pass filter that acts as an anti-alias filter. This setup ensures accurate voltage readings while protecting the circuit from potential spikes. For current inputs, a shunt sense resistor is used, along with anti-aliasing circuitry consisting of resistors and capacitors, to accurately measure current flow. The design allows for a maximum current of 15 A and employs a programmable gain amplifier (PGA) to increase the dynamic range of the ADC.
Wi-Fi SoC Design Considerations
The CC3200 Wi-Fi System on Chip (SoC) plays a crucial role in the smart plug’s design, handling both power management and antenna design. The SoC supports a wide input voltage range and battery power, making it versatile for various applications. However, for the smart plug, a single 3.3 V power rail is used to simplify the design and ensure efficient operation. The CC3200 also features built-in buck converters to power its subsystems, aligning well with the smart plug’s power supply requirements.
Software and Functionality
The software for the smart plug is developed based on FreeRTOS, an open-source real-time operating system. FreeRTOS facilitates task scheduling to manage the various functions of the smart plug, such as querying metrology data, forming data packets, and broadcasting them to a companion Android application. It also manages auxiliary functions and provides bidirectional communication, enhancing the user experience.
Upon power-up, the smart plug initializes by clearing any old profiles and preparing the SPI interface settings. It then enters SmartConfig mode, allowing it to connect to a Wi-Fi network based on existing configurations stored in NVRAM. Users can override this process by pressing a button during startup, forcing the device into a configuration mode for new network settings.
Once connected to a Wi-Fi network, the smart plug sends periodic status messages to the host device via a TCP socket. These messages include device status, power-saving status, and warning alerts for excessive energy consumption. The smart plug uses port 1204 for these communications, ensuring secure and reliable data transmission.
The TIDC-SMARTPLUG-WIFI is a versatile and innovative solution for energy measurement and control, suitable for various applications in smart homes and industrial automation. Its robust design, comprehensive feature set, and ease of use make it an excellent choice for users looking to manage their energy consumption more effectively. With the integration of Wi-Fi connectivity and remote control capabilities, this smart plug represents a significant advancement in the field of connected energy management.
Author Profile
- 20+ years embedded hardware design professional with a burning passion for teaching. Sharing the intricate world of embedded hardware is my mission and joy.
Latest entries
 Tech Updates30 November 2025STM32WBA6: The Next-Generation MCU Powering Secure Short-Range Wireless Designs
Tech Updates30 November 2025STM32WBA6: The Next-Generation MCU Powering Secure Short-Range Wireless Designs Blogs24 November 2025High-Speed PCB Layout Design Guide-104
Blogs24 November 2025High-Speed PCB Layout Design Guide-104 Tech Updates14 September 2025Renesas Launches RL78/L23 Ultra-Low-Power MCUs to Power Smarter Home Appliances
Tech Updates14 September 2025Renesas Launches RL78/L23 Ultra-Low-Power MCUs to Power Smarter Home Appliances Blogs7 September 2025High-Speed PCB Layout Design Guide-103
Blogs7 September 2025High-Speed PCB Layout Design Guide-103